ESG InitiativesInitiatives for Governance
Approach to Promoting Compliance
Basic View on Compliance
GAR has established Basic Compliance Regulations which, in light of the high level of transparency required in the J-REIT business, private real estate fund operation business, and investment advisory business, stipulate basic matters relating to legal compliance that should be implemented by the company, its officers, and its employees in order to appropriately and soundly manage these businesses and, by so doing, establish, maintain, and improve the confidence and trust it has earned from the public, including its clients.
Approach to Promoting Compliance
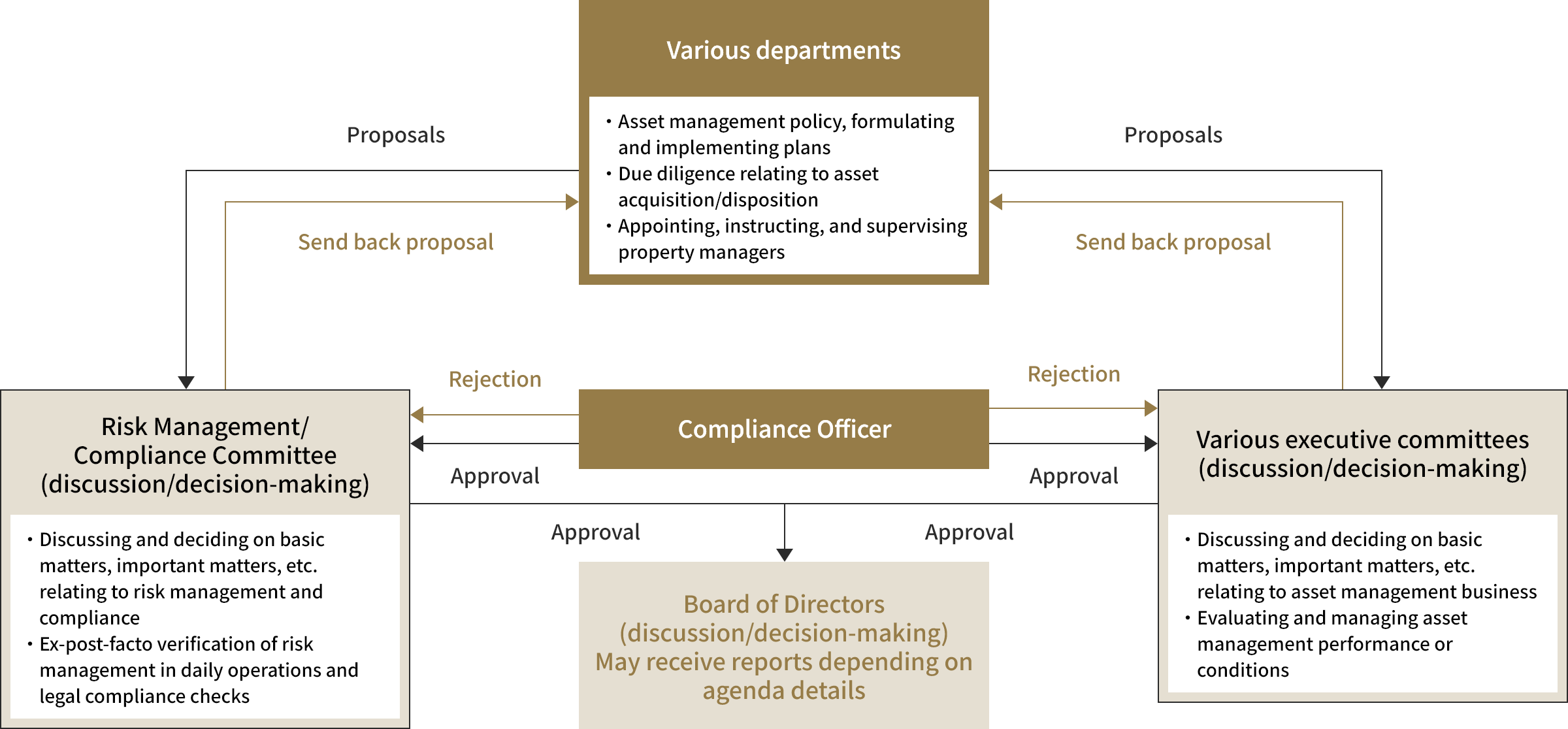
1. Compliance Officer and Compliance Office
GAR has appointed a Compliance Officer as the person responsible for legal compliance. Furthermore, the Compliance Officer oversees the Compliance Office, an organization that independently handles matters relating to GAR's risk management and compliance. In carrying out risk management and compliance checks, the Compliance Officer possesses voting rights for all matters to be resolved by committees and the right of veto for approval requests in daily operations from a compliance view point.
2. Risk Management & Compliance Committee
The Risk Management & Compliance Committee convenes in accordance with the committee regulations stipulated by GAR to discuss and make decisions about matters relating to GAR's risk management and compliance. Action may not be taken on discussed matters without the approval of the Risk Management & Compliance Committee.
3. Compliance Program
Based on the views of the Risk Management & Compliance Committee, the Board of Directors formulates a compliance program for each fiscal year. Furthermore, it promotes the implementation of the compliance program by all officers and employees, including conducting compliance training, internal inspections, and compliance checks based on the program. The Risk Management & Compliance Committee and Board of Directors receive reports on the program's progress status.
4. Compliance Manual
The Risk Management & Compliance Committee has produced a compliance manual for GAR's officers and employees, and takes steps to ensure that they are all cognizant of the importance of adherence to laws, ordinances, etc.
[Checks and balances for decision-making]
Prevention of Conflicts of Interest
1. Prevention of Conflict-of-Interest Transactions with Sponsor-Related Parties
While no interested parties or the like as stipulated by the law exist in GAR, GAR has voluntarily established its own stricter Rules on Transactions with Sponsor-Related Parties. Specifically, these rules prohibit conflict-of-interest transactions with parties such as shareholders who own 5% or more of shares, and if a specified transaction occurs, verification and validation will be carried out to ensure it does not correspond to a conflict-of-interest transaction.
2. Prevention of Conflict-of-Interest Transactions Between Clients Involved in GAR's Three Businesses
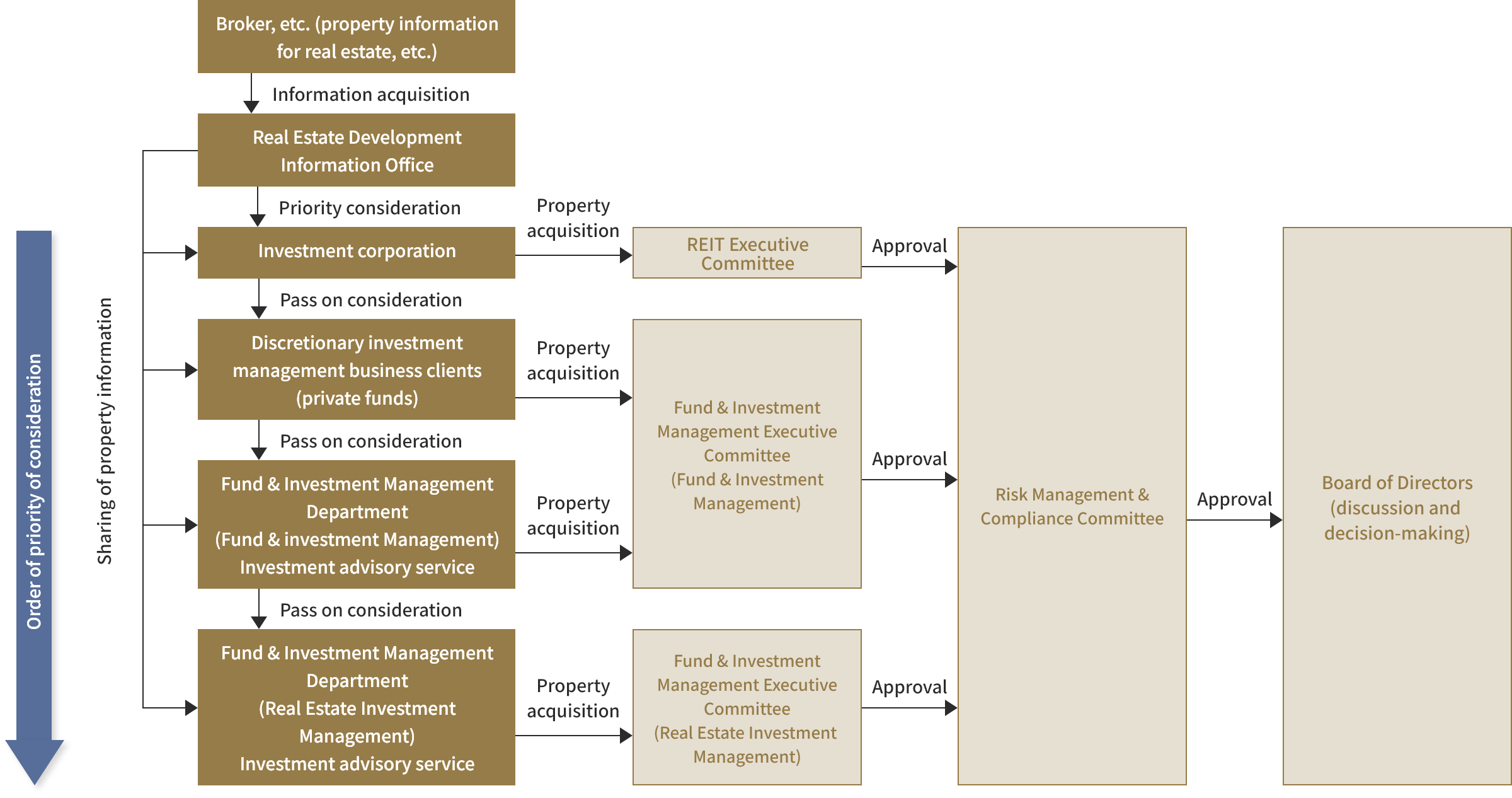
GAR has established internal regulations for the purpose of preventing conflict-of-interest transactions among clients involved in its three businesses. Specifically, while it shares new property information obtained from third parties, the regulations clearly stipulate the order of priority for sharing this information among clients involved in the three businesses at the property acquisition stage. In addition, at the property ownership stage, the regulations stipulate that the intentions of candidate tenants will be dutifully reflected, so that preferential treatment is not given to specific properties without a valid reason, and during property disposition, etc., the regulations rigorously stipulate whether transactions within or among the three businesses are appropriate.
3. Measures to Prevent Management-Related Conflicts of Interest
- 1Independence from sponsors
GAR is not a subsidiary or affiliate of any sponsors. - 2Checks and balances within sponsor groups
The proportion of shares owned by each sponsor group is an equal 14.9%, and because there is one external director from each sponsor group, the relationships are on an equal footing.
[Prioritization Among Clients When Acquiring Properties and Subsequent Flow]
Prevention of Fraud and Corruption (Including Anti-Money Laundering Measures)
In the ethics rules (Code of Conduct), GAR prohibits the giving or receiving of hospitality, money, and goods in dealings with clients that goes beyond the scope of what is appropriate under normal social conventions. Furthermore, these rules also prohibit gifts and hospitality to public employees (including deemed public servants) that infringe the National Public Service Ethics Act, the National Public Service Ethics Code, or other laws and regulations.
In addition, with the establishment of its Basic Policy on Anti-Money Laundering and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT), GAR works to ensure that an appropriate control framework is in place and risk mitigation measures are implemented for combating money laundering and the financing of terrorism (ML/FT).
Specifically, based on its risk-based approach, GAR has a Risk Assessment Report for Transactions with GAR to identify and assess ML/FT risks and implement measures to mitigate such risks. Moreover, GAR has internal regulations stipulating procedures relating to verifying transactions, reporting suspicious transactions, etc., with the aim of preventing ML/FT and thereby ensuring appropriate business activities.
Whistleblowing System
In its Basic Compliance Regulations, GAR specifies that if an employee discovers a case where the laws or regulations are violated (including improper conduct) or at risk of being violated, it is mandatory to report this to a Risk Management & Compliance Manager. It is also possible to report it directly to the Compliance Officer. In addition, the regulations expressly state that employees who report such cases shall not be subject to adverse work conditions or other detrimental treatment due to filing a report.
Information Security
GAR has stipulated internal regulations for the purpose of implementing any measures required to prevent improper use of information assets*, unauthorized access to information assets, and leakage, loss, damage, and other matters relating to the secure management of information assets. As well as ensuring a high level of information security, it has developed an approach that enables the effective use of information assets in its management activities.
*Information assets refers to "information (all electronic and non-electronic information and business-related information recorded by officers and employees and stored in the company, regardless of the storage media) as well as information systems and related assets.""
Approach to Risk Management
Basic View on Risk Management
GAR has established Basic Risk Management Regulations, and as a company engaged in the J-REIT business, private real estate fund operation business, and investment advisory business, which require a high level of transparency, it has established and pursues a sound business management approach based on appropriately managing the risks* that it faces.
*Risks refers to "those factors that involve uncertainties in terms of achieving management targets and business strategy which could potentially cause the loss of management resources or reduce enterprise value by undermining public trust, unless the company understands and effectively manages the uncertainties."
Approach to Risk Management
1. Risk Management & Compliance Committee
The Risk Management & Compliance Committee convenes in accordance with the committee regulations stipulated by GAR to discuss and make decisions about matters relating to GAR's risk management. Action may not be taken on discussed matters without the approval of the Risk Management & Compliance Committee.
2. Risk Management Methods
GAR accurately identifies risks based on an analysis of major risks conducted each fiscal year, as stipulated in the Basic Risk Management Regulations, and implements risk management based on the analysis results.
Specifically, it has created a Risk Analysis Manual for the purpose of conducting this risk analysis, which is implemented using a Risk Analysis Sheet completed by each department and office for each risk it is concerned about, based on the following process: ① determining risk items, ② assessing potential risks, ③ assessing risk management status, ④ assessing remaining risks, and ⑤ future initiatives.
3. Risk Management Status Auditing and Reporting
The President & CEO reports the results of internal audits relating to risk management status conducted by an external auditor to the Risk Management & Compliance Committee, as well as reports designated matters and other necessary matters to the Board of Directors.
4. Addressing the Results of Risk Management-Related Audits
The President & CEO notifies department or office heads of designated matters in internal auditing reports, and the notified department or office heads formulate improvement plans, measures, etc., then promptly submit them to the President & CEO.
Furthermore, the President & CEO convenes meetings of the Risk Management & Compliance Committee to discuss submitted proposals for improvement. If the committee approves a submitted proposal for improvement, it will instruct that the proposal be implemented, and if the proposal is rejected, it will instruct the department or office head to formulate another one.
Approach to Internal Auditing
Basic View of Internal Auditing
GAR has established Internal Auditing Regulations, and in accordance with the basic internal auditing policy stipulated in these regulations, a party that is independent from the departments and offices responsible for carrying out GAR's business (an external auditor) validates the effectiveness of its internal management approach (including the status of risk management and legal compliance), identifies issues with this approach, indicates them, and proposes improvements for the purpose of ensuring the reliability, appropriateness, and soundness of GAR's business.
Internal Auditing Plan
The President & CEO, after taking into account the status of auditing-related risks, creates an internal auditing plan each fiscal year that gives thorough consideration to the importance of the subjects to be audited and other factors and obtains the approval of the Risk Management & Compliance Committee and Board of Directors.
Internal Auditing Result Reporting and Subsequent Response
The President & CEO reports the details of reports about internal audits conducted by an external auditor to the Risk Management & Compliance Committee, as well as reports designated matters and other necessary matters to the Board of Directors.
Furthermore, the President & CEO notifies department or office heads of designated matters in internal auditing reports, and the notified department or office heads formulate improvement plans, measures, etc., then promptly submit them to the President & CEO.
The President & CEO also convenes meetings of the Risk Management & Compliance Committee to discuss submitted proposals for improvement. If the committee approves a submitted proposal for improvement, it will give instructions that the proposal be implemented, and if the proposal is rejected, it will instruct the department or office head to formulate another one.

